Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)
Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)
Sewage is a combination of water and waste which contains organic and inorganic solids from various establishments such as commercial, industrial or residential etc. Hence, cleaning up of wastewater is very much required. Yes, it is the sewage treatment plant (STP) that eliminates harmful contaminants most economically and provides a healthier environment.
Without adequate treatment, sewage will leach into the environment and contaminate ecosystems. For example, sewage contains bacteria and chemicals that break down using oxygen in the water. In doing so, they use oxygen that fish and aquatic life need to survive, so it needs treatment to preserve the ecosystem. Returning sewage/wastewater to a specified quality for safe discharge is the most crucial role of the sewage treatment plant.
We are experts in manufacturing and supplying efficient and cost-effective sewage treatment plant for various sectors in Bangladesh. We have a qualified team who always strives to improve STP design towards a better environment and because of this, we at Sintech Engineering Solutions.
The Benefits of STP
The water we flush down the toilet is turned into potable water, and it is the job of sewage treatment plants to make this water fit for human consumption or release into rivers and oceans.
Here, we let you know the STP or sewage treatment plant advantages.
1. STP is a proven technology that offers reliable performance at all time
2. Sewage treatment plant preserve the natural environment against pollution
3. STP meets the standards for the emission of pollutants set by the Government & avoids heavy penalty
4. Simple and easy installation, low operation, and maintenance of plant
5. Installation of sewage treatment plant reduces risk to public health and the environment
Today’s sewage treatment plants are highly automated, improving plant performance and reducing the risk of human error. Sensor technology, networks and automatic controls keep plants ticking without human intervention.
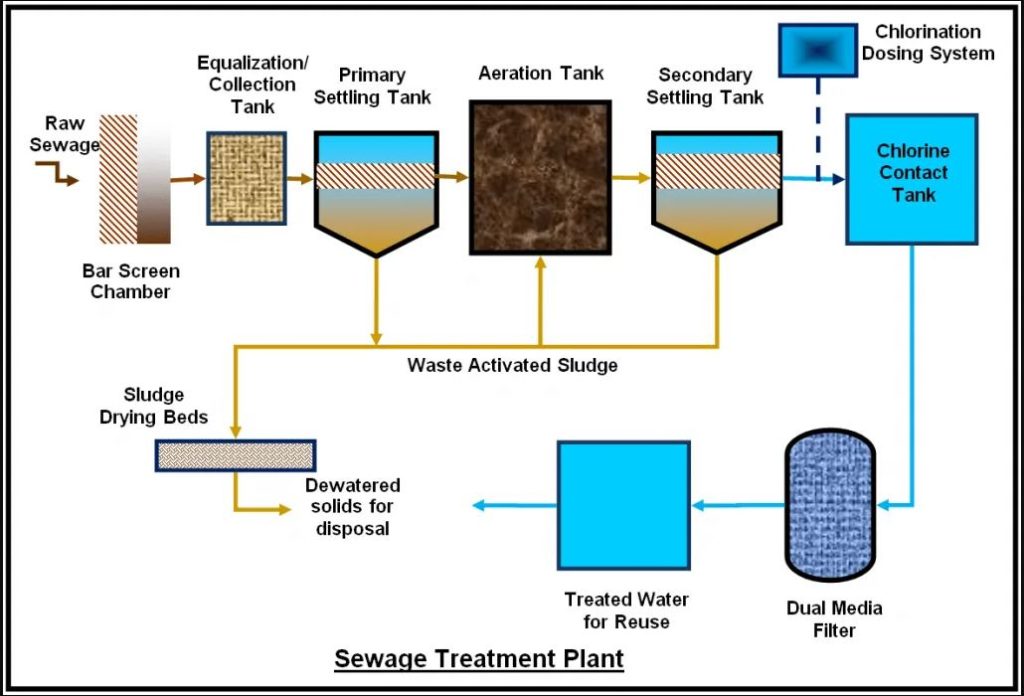
How does a sewage treatment plant work?
Sewage treatment plants run wastewater through multiple treatment stages. After preliminary filtration, there are three main stages of wastewater treatment (primary, secondary, and tertiary), with the third stage reserved for polishing.
Preliminary treatment
Sewage enters the plant network, pushed through various screens to remove large solids and waste, with grit removed by flow attenuation. The purpose of this stage is to filter the sewage of debris, sand, grit, and large particles.
Primary stage
The primary stage involves separating solids from liquids. The sewage is pumped into sedimentation tanks, where gravity forces solids to the bottom of the tank. The water is then released, leaving behind a sludge/slurry.
The sludge is a by-product of primary treatment and can sometimes be repurposed as a fertilizer, but it requires treatment such as de-watering to stabilize it. Incineration is the most likely destination for heavily contaminated sludge.
Secondary treatment
Secondary treatment is the biological treatment stage that breaks down organic contaminants in wastewater.
The two most frequently used processes are activated sludge (aerated ponds) and filter beds (sewage tricked over aggregate), where ‘good’ bacteria in the sludge/aggregate break down the pathogens in the wastewater.
After secondary treatment, wastewater can sometimes be released, providing there’s a low risk to human and animal life and the environment.
Tertiary treatment
Wastewater is considered clean after secondary treatment, but tertiary treatment returns it to an even higher quality for release in protected waters.
The type of tertiary treatment depends on the wastewater. For example, suppose we should release wastewater into bathing or shellfish waters. In that case, it requires disinfection, and nutrients in the water, like phosphorous, must also be removed.
Types of tertiary treatment include:
- Microfiltration (where water passes through tiny holes at high pressure).
- Ion exchange (where ions in the water are exchanged for other ions).
- Activated carbon adsorption (which removes organics).
- Disinfection (where UV light or chemicals kill organic pathogens leftover).
Once the water has been treated, it is typically distributed through a network of pipes to homes, businesses, industries, and other users. The treated wastewater generated during the process is usually further treated to remove pollutants before it is discharged back into the environment, such as rivers or oceans.
Water treatment plants play a crucial role in safeguarding public health by ensuring a reliable supply of clean and safe drinking water, as well as protecting the environment by treating and returning wastewater in a responsible manner.
Sintech Engineering Solutions is an Importer and manufacturer of Sewage Treatment Plant (WTP) in Bangladesh.
Email: sales@sintechbd.com; Cell: 01829-675191
