Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
Effluent Treatment Plant or ETP is one type of wastewater treatment method that is particularly designed to purify industrial wastewater for its reuse and its aim is to release safe water to the environment from the harmful effects caused by the effluent.
Industrial effluents contain various materials, depending on the industry. Some effluents contain oils and grease, and some contain toxic materials (e.g., cyanide). Effluents from food and beverage factories contain degradable organic pollutants. Since industrial wastewater contains a diversity of impurities and therefore specific treatment technology called ETP is required.
The ETP Plant works at various levels and involves various physical, chemical, biological, and membrane processes to treat wastewater from different industrial sectors like chemicals, drugs, pharmaceutical, refineries, dairy, ready mix plants & textile, etc
The Benefits of ETP
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) are used by all leading industries to treat their wastewater. All the leading pharmaceutical, chemical, textile, and other industries that generate wastewater use ETPs to purify water and remove any non-toxic or toxic materials or chemicals from it.
1. To clean industry effluent and recycle it for further use
2. To reduce the usage of fresh water in industries
3. To preserve the natural environment against pollution
4. To meet the standards for the emission of pollutants set by the Government and avoid heavy penalty
5. To reduce expenditure on water acquisition
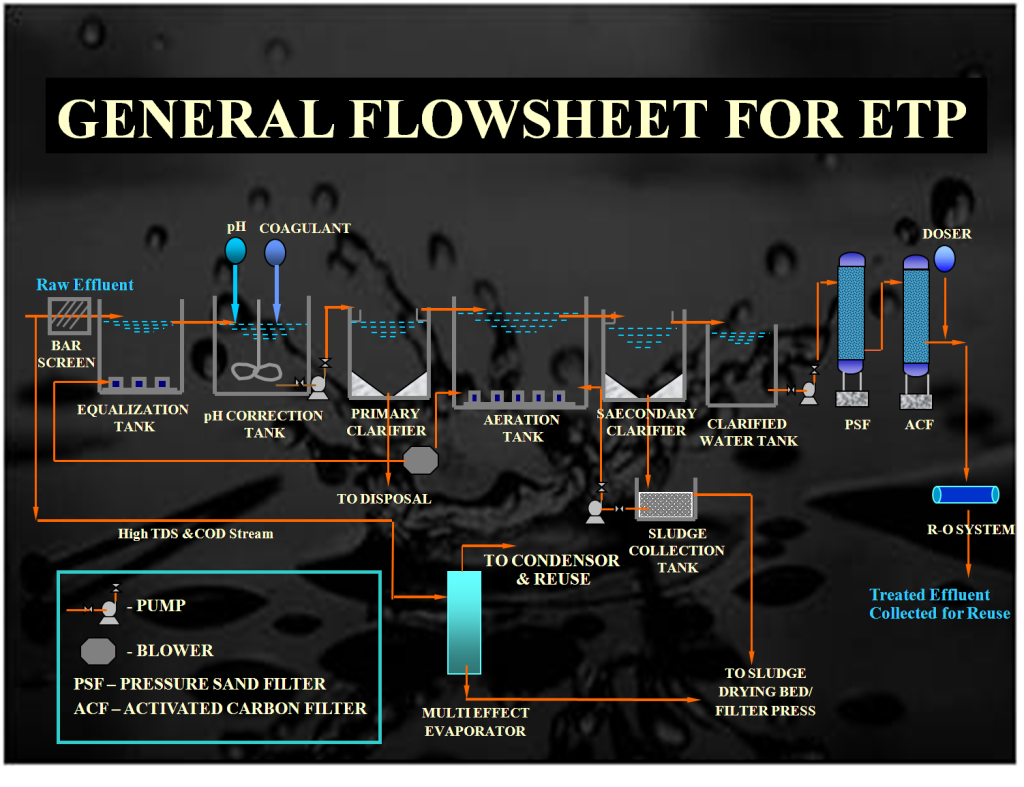
How does ETP Plant Work?
The conceptual approach of the treatment includes the removal of suspended particles, dissolved organic matters and handling of sludge for disposal. Different processes involved are:
Screening: This is the first unit operation that occurs in wastewater treatment plants. A screen is a device with uniform openings and its purpose is to remove large floating solids.
Flocculation: Flocculation is a physical process and does not involve the neutralization of charge. It involves the addition of destabilized particles together into large aggregates so that they can be easily separated from the water.
Coagulation: This is a process in which coagulants are added for the purpose of rapid settlement of minute solid particles in a liquid into a larger mass. It permits particle removal by sedimentation and filtration.
Primary Clarifiers: These are used to slow the velocity of the water to a point where organic solids will settle to the bottom of the tank and it contain equipment that is used to remove floating solids and greases from the surface.
pH CONTROL: The pH value of effluent should be between 5.5 and 9.0, according to the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).pH neutralization is used to modify the pH of the wastewater. For waste that is acidic (low pH),: Bases are used to modify the pH of a solution.
In the case of alkali waste (high pH): Acids are used to modify the pH of a solution.
Primary Clarifier: The primary clarifiers are used to separate settleable solids from the raw incoming wastewater. These are located downstream of the plant. The major function of the primary clarifier is the removal of all settleable and floating solid waste which has a high oxygen demand – BOD.
Aeration Tank: Aeration Tank: An activated sludge process where air is added into the water to encourage microbial growth. The microbes in the water feed on the organic material and form flocs that then settle out. There are two main ways that air is added to the water and they are through blowers and mixers. There are various types of both blowers and mixers.
Aeration is the part of the process that has the most potential recommendations. It is also a rather common practice in industrial applications that can help to reduce BOD.
Possible recommendations are:
- Injecting Pure Oxygen instead of Air
- Replace Coarse Bubble Diffusers with Finer Pore Diffusers
- Install Dissolved Oxygen Probes
- Automatic Dissolved Oxygen Controls
- Replace Positive Displacement with Centrifugal Pumps
- Install on Blowers
Secondary Clarifiers: The secondary clarifiers remove suspended solids and scum present in the effluent from the rotating biological contactor units. The removal of the settleable solids is accomplished by allowing the wastewater to move through the clarifiers at such a reduced velocity that the larger particles settle out.
Applicable areas of ETP:-
- Food and processing industries
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Tannery & Paper industries
- Textile and dye industry
- Dairy and Beverage industries
- Paint Industry
- Chemical Industries, etc.
Our Services:-
Sintech Engineering Solutions has remarkable experience in providing the best end-to-end Water. Our ETP purifies wastewater for its successful reuse and releases safe water into the environment by using physical, chemical, and biochemical processes to get the best possible results from effluent treatment.
Effluent treatment plants play a crucial role in safeguarding public health by ensuring a reliable supply of clean and safe drinking water, as well as protecting the environment by treating and returning wastewater responsibly.
Sintech Engineering Solutions is an Importer and manufacturer of Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) in Bangladesh.
Email: sales@sintechbd.com; Cell: 01829-675191
